What to Do If Raccoons Live in Walls?
Yes, raccoons can live in walls by exploiting structural vulnerabilities such as gaps in roofing, compromised soffits, and attic vents. They choose walls for shelter and protection from predators.
Signs of their presence include nocturnal noises like rustling and scratching, as well as physical damage such as chewed wires and torn insulation. Risks include structural damage, health hazards, and fire dangers from gnawed electrical wires.
Effective removal involves live-trapping and the installation of exclusion devices. Sealing entry points and performing repairs are critical for prevention.
Professionals may be needed for complex cases. Learn more about effective solutions and preventive measures.

Key Takeaways
- Raccoons can live in walls due to structural vulnerabilities like gaps in roofing and compromised soffits.
- Signs of raccoons in walls include nocturnal sounds like rustling and scratching.
- Raccoons choose walls for shelter, warmth, and protection from predators.
- Risks of raccoons in walls include structural damage, health hazards, and fire risks from gnawed electrical wiring.
- Humane removal involves live-trapping, exclusion devices, and sealing entry points to prevent re-entry.
How Raccoons Enter Homes
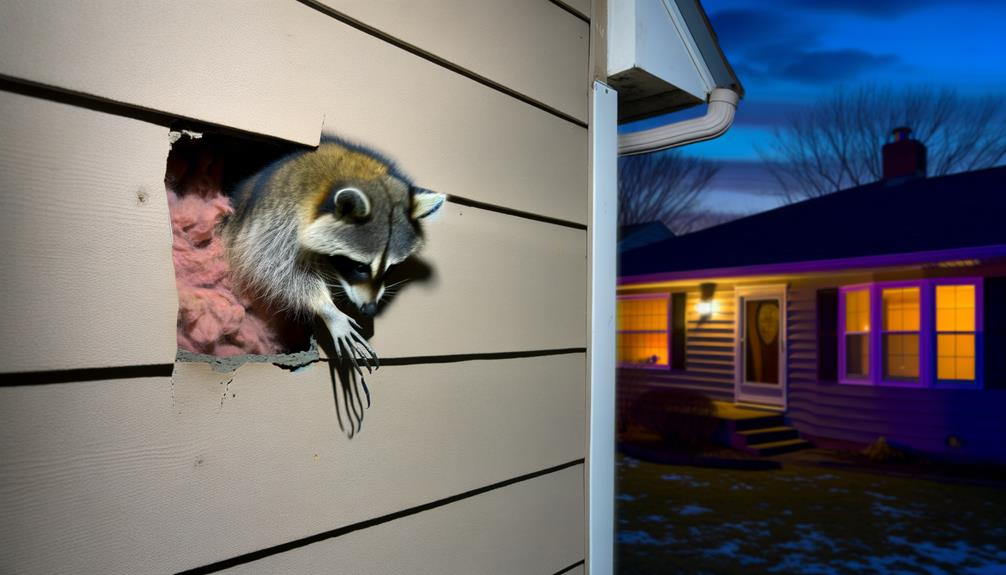

Raccoons typically enter homes through structural vulnerabilities such as gaps in roofing, uncapped chimneys, or compromised soffits. These agile mammals exploit even minor openings to gain access, often drawn by the search for food, shelter, or a safe nesting site.
Roof intersections, eaves, and attic vents are common entry points where raccoons can create or enlarge existing gaps. Their dexterous paws enable them to manipulate loose shingles or fascia boards effectively. Additionally, raccoons may utilize downspouts or climbing vegetation to reach elevated entries.
Once inside, they can cause significant damage, including insulation displacement and electrical wiring disturbances. Understanding these entry methods is essential for implementing preventive measures to safeguard residential structures from raccoon intrusions.
Signs of Raccoons in Walls
Identifying the presence of raccoons within wall cavities can be achieved through careful observation of nocturnal activity sounds and unusual wall damage. Nocturnal activity sounds may include scratching, thumping, or chirping noises, which are typically more prominent at night due to the raccoon's active period.
Additionally, unusual wall damage, such as holes, dents, or claw marks, may indicate entry points or attempts to create nesting areas within the walls.
Nocturnal Activity Sounds
During nighttime hours, distinctive rustling, scratching, and scurrying sounds within the walls may indicate the presence of raccoons. These nocturnal creatures are known for their active behavior during the night, leading to noticeable auditory signs for homeowners.
The specific sounds can often be categorized as:
- Rustling: The noise of raccoons moving through insulation or other materials.
- Scratching: The sound of claws against wooden beams or drywall.
- Scurrying: Rapid movements, suggesting multiple raccoons are present.
These auditory cues are vital for identifying a raccoon infestation, as the animals are primarily active after dusk. Recognizing these sounds early can aid in prompt intervention, minimizing potential damage and health risks associated with raccoon habitation within residential walls.
Unusual Wall Damage
Observable signs of raccoons inhabiting walls often include unusual damage such as chewed wires, torn insulation, and compromised structural integrity. These signs can indicate raccoons' presence due to their tendency to gnaw on electrical wiring, which poses a fire hazard. Additionally, raccoons may pull apart insulation for nesting, leading to reduced energy efficiency and increased heating or cooling costs. Structural damage can occur as raccoons create entry points or enlarge existing gaps in walls.
| Damage Type | Potential Effects |
|---|---|
| Chewed Wires | Fire hazards, electrical outages |
| Torn Insulation | Reduced energy efficiency, higher costs |
| Compromised Structure | Weakening of walls, entry points for pests |
| Scratches and Marks | Visible surface damage, aesthetic issues |
Understanding these signs can facilitate timely intervention and prevent further damage.
Why Raccoons Choose Walls
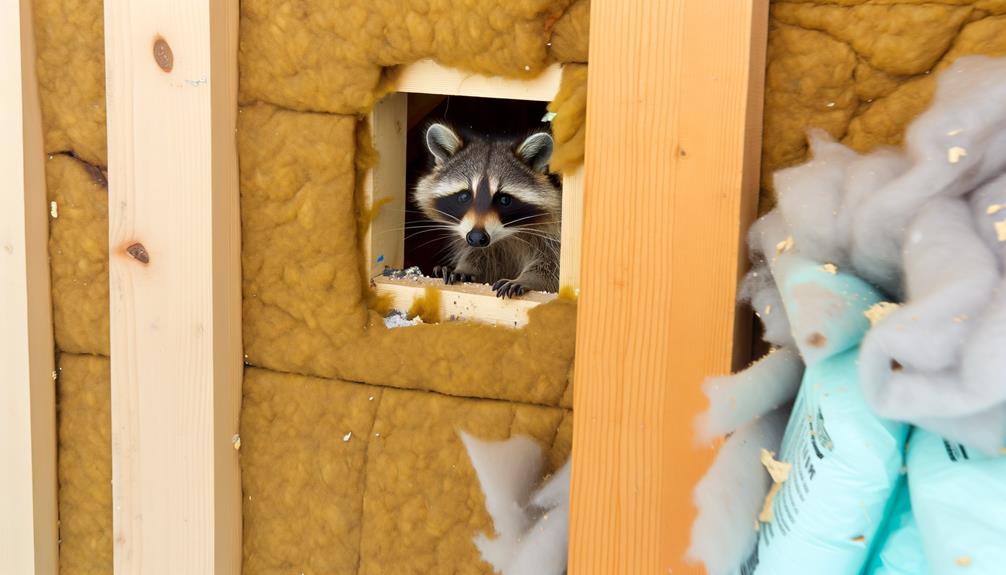

Raccoons are attracted to wall cavities primarily due to the protection these structures offer against predators and environmental hazards. The enclosed space provides a stable, warm environment that is essential for their survival, particularly during colder months.
Additionally, walls offer a safe nesting site, reducing the risk of threats to their offspring.
Shelter From Predators
One primary reason raccoons choose to inhabit walls is the significant protection these structures offer against potential predators. The enclosed spaces within walls act as formidable barriers, making it difficult for larger predators to access these areas.
This defensive advantage can be particularly vital in urban environments where raccoons face threats from domestic dogs, which are unable to penetrate the confined spaces of walls. Birds of prey, which cannot navigate the narrow, enclosed areas, and coyotes and other large mammals, which are deterred by the structural integrity of walls.
Warmth and Safety
In addition to providing protection from predators, walls also offer raccoons a warm and secure environment, which is vital for their survival, especially during colder months. The insulation properties of walls help maintain a stable internal temperature, shielding raccoons from harsh weather conditions. This warmth is particularly essential for females nursing their young, as it ensures the pups' development in a controlled environment. Additionally, the structural integrity of walls provides a safe haven from potential threats.
| Factor | Description | Benefit to Raccoons |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | Maintains stable internal temperature | Warmth during colder months |
| Structural Integrity | Solid, enclosed space | Protection from external threats |
| Controlled Environment | Consistent, secure setting | Safe rearing of offspring |
These factors collectively contribute to the appeal of walls for raccoons seeking warmth and safety.
Risks of Raccoons Indoors
The presence of raccoons within the walls of a home presents significant risks, including structural damage, health hazards, and potential contamination from their waste. These nocturnal creatures can cause substantial harm by gnawing on electrical wiring, which poses a fire risk. Additionally, raccoons can carry zoonotic diseases such as rabies and leptospirosis, endangering human health.
Structural Damage: Raccoons often tear insulation and chew through wood, weakening the structural integrity.
Health Hazards: Their droppings may harbor pathogens, including roundworm eggs, which can become airborne and cause severe infections.
Contamination: Accumulated waste materials can lead to foul odors and attract other pests, creating an unsanitary living environment.
Understanding these risks is essential for effective wildlife management.
Identifying Entry Points
To mitigate the risks associated with raccoons indoors, identifying their entry points is a critical step. Raccoons often exploit structural vulnerabilities such as broken vents, uncapped chimneys, and gaps in roofing materials.
These animals are adept climbers, making roof edges and soffits particularly susceptible. Additionally, raccoons can enlarge existing small openings to gain access. Conduct a thorough external inspection of the property, focusing on areas where building materials converge, such as corners and intersections of walls and roofs.
Pay special attention to any signs of gnawing or claw marks, which indicate recent activity. Properly identifying and sealing these entry points is essential to prevent raccoons from infiltrating and residing within wall cavities or attics.
Inspecting for Raccoon Presence
A systematic inspection for raccoon presence involves checking for telltale signs such as droppings, nesting materials, and tracks around potential entry points and within attics or wall cavities. Raccoons often leave behind distinct evidence that can be identified through careful observation.
Key indicators include:
- Droppings: Typically found along walls or in corners, raccoon feces are cylindrical and may contain undigested food.
- Nesting Materials: Look for shredded insulation, leaves, or paper that raccoons use to create their nests.
- Tracks: Raccoon footprints are identifiable by their five fingers and toes, often visible in dusty or soft surfaces near entry points.
Properly identifying these signs guarantees accurate detection, facilitating appropriate intervention measures.
Humane Removal Methods
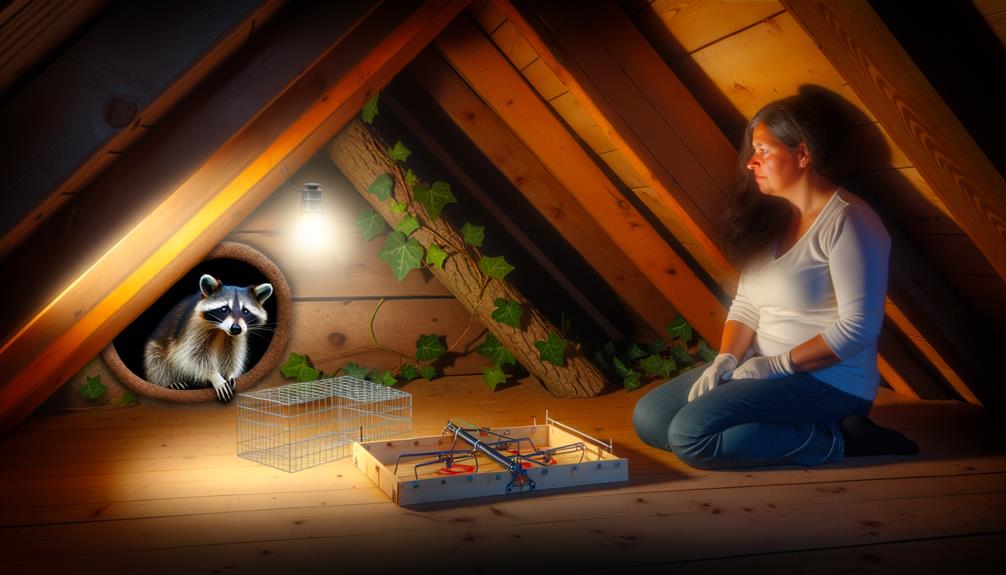

When addressing the humane removal of raccoons from wall cavities, it is essential to take into account both live-trapping techniques and the installation of exclusion devices.
Live-trapping involves capturing the raccoon in a manner that minimizes stress and harm, followed by its relocation to a suitable habitat.
Exclusion devices, such as one-way doors, guarantee that raccoons can exit the wall space but are unable to re-enter, effectively preventing future infestations.
Live-Trapping Techniques
Implementing live-trapping techniques demands a thorough comprehension of raccoon behavior and the use of specialized equipment designed to safely and humanely capture the animals.
Effective live-trapping involves:
- Bait Selection: Using foods such as marshmallows or cat food, which are highly appealing to raccoons.
- Trap Placement: Strategically situating traps in areas with high raccoon activity, such as near entry points or along raccoon pathways.
- Monitoring and Timing: Regularly checking traps to guarantee captured raccoons are not subjected to prolonged stress or adverse weather conditions.
These steps are essential to minimize harm and guarantee the ethical treatment of raccoons during removal.
Properly executed, live-trapping provides a humane solution to raccoon infestations, aligning with best practices in wildlife management.
Exclusion Device Installation
Effective exclusion device installation requires a detailed understanding of raccoon entry points and behavior to guarantee humane removal and prevent future infestations. To achieve this, professionals must first conduct a thorough inspection to identify all potential access points, including gaps in walls, vents, and chimneys.
One-way exclusion devices, which allow raccoons to exit but not re-enter, are then strategically installed at these identified locations. These devices must be monitored and maintained to make sure they function correctly and do not cause undue stress or harm to the animals.
Following removal, all entry points should be securely sealed using durable materials to prevent re-entry. This all-encompassing approach ensures both the humane treatment of raccoons and the long-term protection of the property.
Preventing Future Infestations
Preventing future infestations of raccoons involves thorough inspection and sealing of potential entry points in building structures. Detailed examination of the roof, attic, vents, and foundation is crucial to identify vulnerabilities.
Effective raccoon-proofing strategies include:
- Sealing Gaps and Cracks: Use durable materials such as steel mesh or concrete to block any openings that raccoons could exploit.
- Installing Chimney Caps: Securely fitted caps prevent raccoons from entering through chimneys.
- Maintaining Yard Hygiene: Regularly removing food sources and securing garbage bins reduces attractants for raccoons.
These measures, combined with regular monitoring, are essential to guarantee raccoons do not re-establish residence within the walls. Adopting a proactive approach can mitigate potential infestations, safeguarding both the structure and its occupants.
Repairing Wall Damage
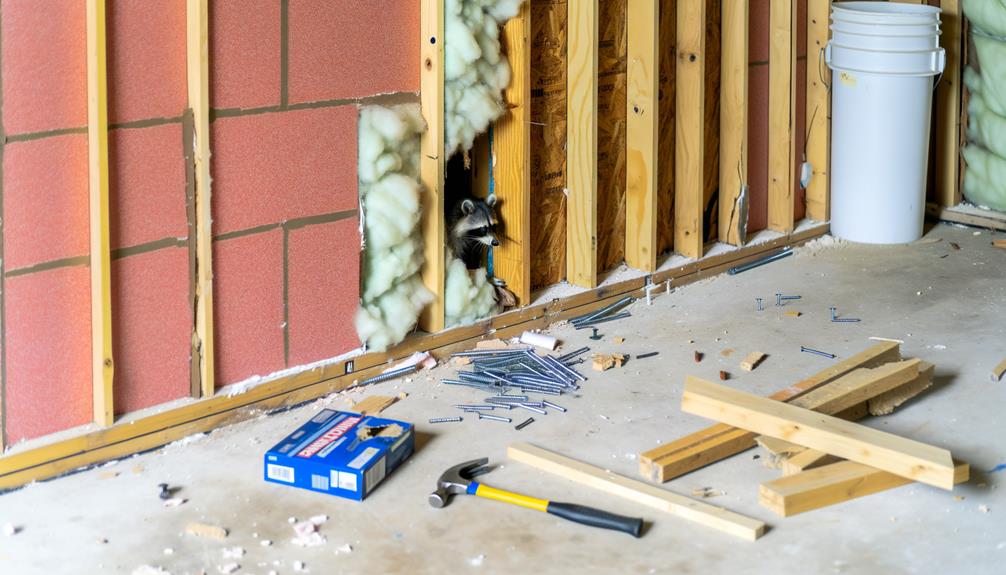

Addressing the damage caused by raccoons within walls requires a systematic approach to restore structural integrity and prevent further degradation. Initially, a thorough inspection is essential to assess the extent of the damage. This includes identifying gnawed wires, insulation displacement, and compromised wallboards. Once the assessment is complete, removal of contaminated materials is necessary to prevent mold and odor issues. Following removal, repairs should involve replacing insulation, fixing wiring, and patching wallboards. Finally, sealing entry points is critical to prevent re-entry and future infestations.
| Damage Type | Emotional Impact | Required Action |
|---|---|---|
| Gnawed Wires | Concern for Safety | Electrical Repairs |
| Displaced Insulation | Anxiety over Energy Efficiency | Replacement of Insulation |
| Compromised Wallboards | Distress over Aesthetics | Wallboard Repair and Painting |
When to Contact Professionals
Engaging expert wildlife removal services becomes crucial when the infestation poses significant health risks or when structural damage exceeds the scope of typical homeowner repairs. Professionals have the expertise to handle complex situations involving raccoons in walls, guaranteeing thorough and safe removal.
Indicators necessitating expert intervention include:
- Health Risks: Raccoons can carry diseases such as rabies and leptospirosis, posing significant health hazards to inhabitants.
- Structural Damage: Persistent gnawing and nesting can compromise the integrity of insulation, wiring, and wood structures, requiring expert repairs.
- Complex Infestations: Multiple entry points or inaccessible nesting areas within walls often require specialized knowledge and equipment for effective resolution.
Contacting specialists ensures the situation is managed efficiently, minimizing risks and preventing recurrence.
Conclusion
To sum up, the presence of raccoons within walls poses significant challenges, including structural damage, health risks, and potential safety hazards.
Understanding the methods by which these animals infiltrate homes, recognizing the signs of their presence, and implementing humane removal and preventive strategies are paramount.
Such measures not only mitigate risks but also promote coexistence with wildlife.
Just as a fortress is fortified against invaders, homes must be safeguarded against the intrusion of raccoons to guarantee structural integrity and occupant safety.






